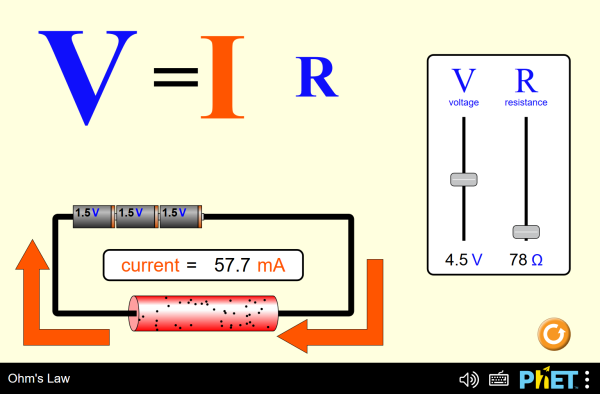
Ohm's Law - Relationship between current and voltage.

⇒
Here , when the Potential difference of 0 voltage is applied the
ammeter in the circuit reads 0 amps , when it is increased to 5 voltage
the ammeter reads 1 amps which is verified using the formula  and so on , which is in accordance with the ohm law which states that
the current flowing the circuit is directly proportional to the
potential difference applied when the resistance is kept constant....Read more https://electronicspani.com/ohms-law/
and so on , which is in accordance with the ohm law which states that
the current flowing the circuit is directly proportional to the
potential difference applied when the resistance is kept constant....Read more https://electronicspani.com/ohms-law/
- The voltage across an element is directly Proportional to the current flowing.
Thus: v=iR and R/i
Where: R=resistor ⇒ Has ability to resist the flow of electric current.

Take note:
- Resistors has no polarity
- Not flows - to +
- The value of R :: Varies from 0 to infinity
- Extreme values == 0 and infinity
- Only linear resistors obey ohm's law
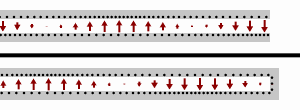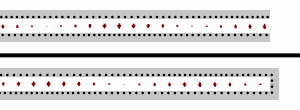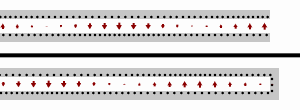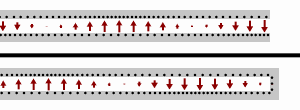
- The
transmission lines, the top one terminated at an open circuit, the
bottom terminated at a short circuit. Black dots represents electrons,
and the arrows show the electric field.
[gallery ids="283,284" type="rectangular"]
CONDUCTANCE
⇒ The ability to conduct electric current flow.
- unit (mho) or (siemens)
- symbol S
- Reciprocal of the resistance R (G= 1/R)
POWER

- R and G are positive quantities, thus power is always POSITIVE.
- R absorbs power from the circuit → PASSIVE ELEMENT
EXAMPLE 1
- Determine voltage (v), conductance (G) and power (p) from the figure below.
 Solution:
Solution:
For voltage:
v=iR
=(2*10^-3)(10*10^3)
v=20V
For Conductance:
G=i/R
=1/10*10^3
G=1*10^-4
For Power:
P=t^2R
=v^2/R
=(2*10^-3)^2 (10*10^3)
=0.04 w
=40mW
=(20)^2/10*10^3
P=0.04 w
EXAMPLE 2
- Calculate current i in figure below when the switch is in position 1.
- Find the current when the switch is in position 2.
 Solution:
(a) i = 3/100 = 30 mA
(b) i = 3/150 = 20 mA
Solution:
(a) i = 3/100 = 30 mA
(b) i = 3/150 = 20 mA
LEARNING/SUMMARY
Everything
around us is connected or related with each other. So, therefore, in
dealing with circuit analysis, everything is also related. One element
might be directly proportional. It could be that another element is
inversely proportional to the other. But the point is, if one has been
measured or calculated mistakenly, everything will be reversed to be
wrong.
So,
therefore, if you have not understood the basics, it would be hard for
you to go through. So, go back to the previous lessons and come back to
deal with this topic.
TRY THIS! ↓↓↓
https://phet.colorado.edu/sims/html/ohms-law/latest/ohms-law_en.html
Basic Concept (Chapter 1)
Any
engineering courses related with electricity must study and understand
the fundamentals of electric circuits as students enter in their major
subjects.
Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Introduction
Electric circuit and electromagnetic theories are two fundamental theories upon which all branches of electrical engineering are built.
WHY DO WE NEED TO STUDY "BASIC ELECTRIC CIRCUIT"?
- This
is because everything starts with the BASICS. We cannot jump up to the
hardest fields without dwelling with the penny matters. Basic electric
circuit is the most important course for electrical engineering students
and even electronics and computer engineering courses education.
- This is valuable for students like us who are specializing in other branches of the physical sciences because circuits are good model for the study of energy systems in general, and because of the applied mathematics, physics, and topology involved.
What is Electric Circuit?

- Fig. 1
An
Electric Circuit is an interconnection of electrical
elements. Electric circuit theory and electromagnetic theory are the two
fundamental theories upon which all branches of electrical engineering
are built.
Its function is to transfer energy from one point to another or from one element to another element.
Fig.
1 This is an example of a simple Electric Circuit. It has battery,
switch and the bulb. When you turn on the switch with a closed loop the
current flows and the bulb will light up.
BASIC ELEMENT
Charge- q(t)
It refers to the basic quantity in an electric circuit.
ELECTRICAL PROPERTY OF MATERIALS
- Exist (Electron) which is negative and (Proton) positive
- Measured in Coulombs (C)C
- One electron has a charge of -1.602 * 10 ^-19 C
Current- i(t)
- It refers to the charge flow rate
- It is measured in Ampere (A)
- 2 types: DC (Direct Current) and AC (Alternating Current)

Voltage- v(t)
- It refers to the charge rate of doing work
- Energyrequired to move a unit charge through an element
- Measured in volts (V)
Power- p(t)
- It refers to time rate of doing work
- Measured in watts (w)
Power can be absorbed or supplied by circuit elements
- positive power- element absorbs power
- negative power- element supplies power
- 'sign' determined by voltage and current
- An ideal circuit is ΣPsupplied + ΣPabsorbed = 0
Energy
It is the capacity to do work
Circuit Elements
- An element is the basic building block of a circuit
- Electric circuit is interconnecting of the elements
Types of Elements:
- Active elements- capable of generating energy
- Passive elements- absorbs energy
Source
- Independent Source- does not depend to other elements to supply voltage or current.
- Dependent Source- Depend to other elements to supply Voltage or Current.
Example Exercises (1)
- Determine the current flowing through an element if the charge flow is given by: q(t) = (9t² +2t-2) C
Solution:
q(t)= 9t²+2t-2 C
dq/dt= 18t+2
i(t)=dq/dt =18t+2
- Find the charge q(t) flowing through a device if the current (i(t)) = (2t + 5) mA and q(0)=0
Solution:
i= dq/dt q(0)=0
∫dq= ∫i dt q(0)= t²+5t+C =0
q= ∫i dt =0²+5(0)+C
q= ∫ (2t+5) dt =0
q(t)= t²+5t+C Therefore, the charge is 0.
- The change entering a certain element is shown. Determine the current at:
(a) t = 1 ms
(b) t = 6 ms
(c) t = 10 ms
 Solution:
(a) At t = 1ms, i= dq/dt
=80/2
=40A
(b) At t = 6ms, i= dq/dt
=0A
(c) At t = 10ms, i= dq/dt
=80/4
=20A
Solution:
(a) At t = 1ms, i= dq/dt
=80/2
=40A
(b) At t = 6ms, i= dq/dt
=0A
(c) At t = 10ms, i= dq/dt
=80/4
=20A
LEARNING/SUMMARY
- In
analyzing or dealing with circuits, it is really better for us to know
what are the concepts under every thing. We must know how everything
works, how each element affects the whole circuits and how conscious we
should be in taking part of analyzing the circuit. Because if we fail to
do this, we will be failure at all level regarding circuit analysis.
- It
is important to know the basic elements of the circuit because it is
always the best to start with the basics since it is the foundation in
solving or dealing problems as we go through our journey to be
electrical and electronics engineers.
- Each element is co-related with one another. They might be directly proportional or inversely proportional with each other.